The rapid expansion of immersive technologies is revolutionizing tourism, particularly in museums, exhibitions, and cultural attractions. Multisensory extended reality (XR) design is at the forefront of this transformation, offering visitors experiences that transcend traditional boundaries. Across the globe, cities are embracing these innovations, with new immersive exhibitions emerging regularly. Prominent examples include the Illusionaries exhibition and the permanent exhibit at Canary Wharf in London, the free-admission Outernet on Charing Cross Road in London, and the Sphere in Las Vegas. These attractions demonstrate how XR technologies can create captivating, multisensory experiences that engage and delight audiences, setting the stage for the future of tourism.
The tourism industry stands on the edge of a transformation, driven by the integration of immersive multisensory technologies (Santoso, Wang & Windasari 2022). This innovative approach to creating captivating tourist attractions and experiences provides a significant leap from traditional experiences, promising a new era of engagement and value creation for visitors worldwide. The heart of this transformation lies in the convergence of three paramount research domains: value creation (e.g. Smith & Colgate 2007), multisensory experience (e.g. Agapito 2023), and immersive XR technologies (e.g. Buhalis et al. 2022). This exploration unveiled the rich potential of XR in transforming the tourism landscape, offering insights grounded in comprehensive academic investigation and practical applications alike.
The journey of discovery
The journey begins with an examination of how value is created within the tourism context, a concept that has long fascinated scholars and industry practitioners. Smith and Colgate’s (2007) framework, emphasizing the experiential value stemming from sensory, emotional, epistemic, and social interactions, serves as a cornerstone for understanding the nuanced process of value creation in tourism.
As we delve into the multisensory mixed-reality tourism context, a notable gap in the literature emerges. While the influence of the physical environment on consumer satisfaction is well-documented, the advent of immersive technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) introduces a new dimension to the experience. These technologies not only enhance the sensory engagement but also enrich the emotional and cognitive aspects of the tourist journey, offering an unparalleled depth of immersion.
The power of sensory immersion
In an era where technology shapes every facet of our lives, the tourism industry is no exception. The impact of multisensory experiences on value creation is profound, as evidenced by numerous global applications. Extended Reality Environments (XRE) significantly influence visitors’ perceptions, crafting a multisensory landscape that heightens emotional involvement and shapes behavioural intentions.
A conceptual framework, such as the innovative Stimuli-Immersion-Value-Action (SIVA) Model (Tuominen 2023), encapsulates the effects of multisensory mixed-reality cues on visitors’ behavioural intentions. This model underscores the transformative power of XR atmospherics and XR experience in fostering sensory immersion and enhancing hedonic value, thereby shaping the future of tourism attractions.
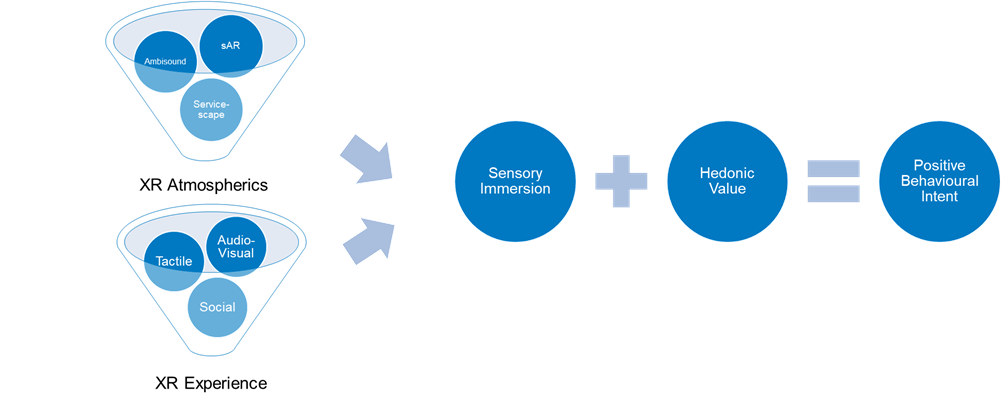
Picture 1. Impact of XR tech on sensory immersion and perceived hedonic value (Source: Authors’ own)
The SIVA Model, as illustrated in the diagram, provides a comprehensive framework for understanding how multisensory extended reality (XR) environments can enhance visitor experiences and influence their behaviour. Below is a detailed explanation of the model.
Stimuli
The model begins with Stimuli, which includes two main components: XR Atmospherics and XR Experience. XR Atmospherics refers to the environmental enhancements within an attraction or museum that create an immersive atmosphere. It may include e.g.:
- Ambisound: The use of spatial audio to create a 3D sound environment.
- Spatial Augmented Reality (sAR): Also known as projection mapping, this involves projecting images and videos onto physical spaces to create dynamic, interactive visuals.
- Servicescape: The overall physical environment where the experience takes place, designed to enhance the sensory experience.
- XR Experience component focuses on the interactive aspects that allow visitors to engage with the environment. It includes:
- Tactile: Interfaces that provide physical interaction through touch.
- Audio-Visual: Interactive visual and auditory elements that respond to visitor actions.
- Social: Opportunities for social interactions with other visitors, enhancing the communal aspect of the experience.
Sensory Immersion
The Stimuli positively influence Sensory Immersion, which represents the depth of engagement and involvement a visitor feels within the experience. High sensory immersion means that visitors are deeply absorbed and captivated by the multisensory environment.
Hedonic Value
Heightened Sensory Immersion leads to an increase in Hedonic Value. This term refers to the pleasure and enjoyment derived from the experience. Decades of research in tourism have shown that hedonic value is a fundamental element of memorable tourism experiences. When visitors perceive high hedonic value, they find the experience highly enjoyable and satisfying.
Action (Positive Behavioural Intent)
Finally, a high level of Hedonic Value translates to Positive Behavioural Intent. This may include:
- Repeat and Increased Purchase Behaviour: Visitors are more likely to return and spend more money.
- Intention to Recommend: Satisfied visitors are more likely to recommend the experience to others.
- Intention to Revisit: Positive experiences increase the likelihood that visitors will come back.
In essence, the SIVA Model illustrates how XR atmospherics and experiences create powerful sensory immersion, which enhances the perceived enjoyment of the experience. This heightened enjoyment leads to positive behavioural outcomes, such as repeat visits, recommendations, and increased spending. By understanding and applying this model, attractions and museums can design more effective and engaging XR experiences that delight visitors and foster long-term loyalty.
Philosophical underpinnings
Drawing on the philosophical insights of Aristotle and Plato, the role of sensory experiences in shaping human cognition and perception is profound. This perspective enriches our understanding of how multisensory extended-reality environments can offer more than just entertainment—they can profoundly impact our perception of value and enjoyment.
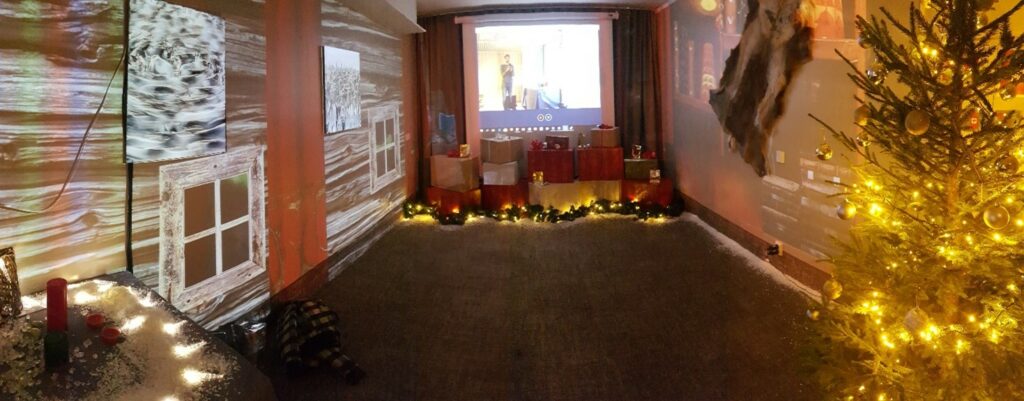

Picture 2. Virtual Elf’s House concept combining multisensory stimuli (temperature, scents, sounds and video) for a unique and interactive Santa Claus on-line visit. (authors own 2021)
For tourism developers, marketers, and XR developers, these insights offer a blueprint for harnessing the potential of multisensory spatial augmented reality and multisensory interaction through haptic interfaces and immersive soundscapes. The integration of these technologies not only enriches the tourist experience but also enhances engagement and satisfaction, paving the way for a new era of immersive tourism attractions.
The significance of sensory elements in creating memorable experiences highlights the need for thoughtful integration of visual, auditory, olfactory, gustatory, and tactile stimuli. This approach captivates visitors and fosters a deeper connection with the destination, ultimately shaping their perceptions and behaviors.
In summary, the critical importance of seamlessly integrating technology and storytelling, enhancing multisensory experiences, fostering emotional engagement, and innovatively utilizing space are vital for creating immersive and impactful tourism experiences. Collaborative efforts with experts in storytelling and technology further elevate the quality of these experiences.
At Haaga-Helia University, we are pioneering the development of XR experiences for esteemed partners like Lapland Safaris, Finlandia Hall, Haltia Nature Centre, Visit Finland, and the Manchester United Museum. Our work demonstrates how these principles can be applied to create captivating and memorable tourist attractions, setting new benchmarks for the industry.
As we gaze into the future, it is clear that the intersection of multisensory experiences and extended-reality technologies holds infinite possibilities for the tourism industry. By embracing these innovations, we can create enchanting, immersive worlds that not only entertain but also enrich our understanding of the world around us. The journey of discovery is just beginning, and the horizon is filled with opportunities to transform the way we experience tourism in the digital age.
Key managerial takeaways
1. Seamless Integration of Technology and Storytelling
Ensuring that technology enhances rather than overshadows the narrative can create more engaging and memorable experiences. Developers should focus on how technology can serve the story, making it more immersive and emotionally impactful.
2. Multisensory Experiences
Incorporating multisensory elements can significantly enrich visitor experiences. This approach aligns with contemporary research emphasizing the importance of sensory engagement in tourism and destination design.
3. Emotional Engagement
Effective use of technology, like projection mapping and spatial audio, can evoke strong emotions, deepening the audience’s connection to the story. Emotional resonance is crucial for creating lasting impressions.
4. Innovative Use of Space
Creative stage and exhibit design can transform ordinary spaces into extraordinary experiences. Attention to detail and innovative use of technology can make environments more dynamic and engaging.
5. Collaborations and Partnerships
Collaborating with experts in storytelling and technology can elevate the quality of the experience. Partnerships can bring in diverse skills and perspectives, enhancing the final product.
The article is based on the author’s doctoral dissertation Measuring the Effects of Multi-Sensory Stimuli in the Mixed Reality Environment for Tourism Value Creation, Tuominen P, 2023, Manchester Metropolitan University and leans heavily on theBox immersive learning environment initiative. Since 2016, theBox at the Haaga campus of Haaga-Helia UAS has led educational efforts in blending new technologies, storytelling, and experience design for students and professionals in tourism, hospitality, and experience sectors. The author has nearly a decade of experience in creating tech driven immersive experiences for international firms and Haaga-Helia UAS partners.
XRexp – the XR experience path and embedded multi-channel commerce solutions project brings together new technology companies to develop experiential services and multi-channel commerce at Finlandia Hall and other visitor attractions. The project promotes the development of an innovation ecosystem of cultural and XR technology companies and explores which technologies and equipment are best suited to the identified target customer groups. The end result will be a description of an optimal XR experience pathway to inspire new networking and future design work. The project is funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and the Helsinki-Uusimaa Regional Council.


References
Agapito, D. 2023. Tourism, senses and well-being. In Geography of Happiness: A Spatial Analysis of Subjective Well-Being (pp. 161-176). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Buhalis, D. and Karatay, N. 2022. ‘Mixed Reality (MR) for Generation Z in Cultural Heritage Tourism Towards Metaverse.’ In Stienmetz, J.L., Ferrer-Rosell, B., and Massimo, D. Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2022 Proceedings of the ENTER 2022 eTourism Conference. Cham: Springer, pp. 16-27.
Santoso, H. B., Wang, J. C. & Windasari, N. A. 2022. Impact of multisensory extended reality on tourism experience journey. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology, 13(3), 356-385.
Smith, J. B., and Colgate, M. 2007. ‘Customer value creation: a practical framework.’ Journal of marketing Theory and Practice, 15(1) pp. 7-23.
Main picture: Shutterstock